3 gnuplotを使ったグラフ表示
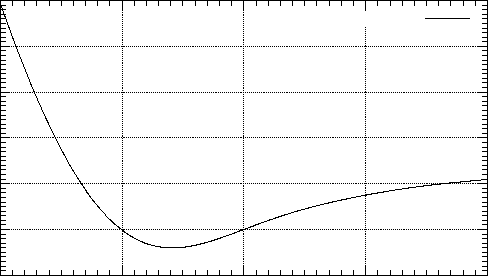
グラフ表示を行った後,二分法により方程式の解を計算するプログラムをリスト 2に示す.このプログラムを実行すると,図 1のようなグラフが表示された後,近似解が,answer = -1.5479375e+00と表示される
次年度以降,ここで学習したC言語の知識を他の科目で応用しようとする者は,このプロ グラムを理解せよ.そして,自分で書いて見よ.
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <math.h>
3 #define EPSILON (1.0e-10)
4
5 double function(double x);
6 double bisection(double (*f)(), double left, double right);
7 void mk_data(char *a, double (*f)(), double x1, double x2, int n);
8 void mk_graph(char *f, char *xlb, double x1, double x2,
9 char *ylb, double y1, double y2);
10
11 /*==========================================================*/
12 /* main function */
13 /*==========================================================*/
14 int main(void){
15
16 double left, right, ans;
17
18 left=-2.0;
19 right=2.0;
20
21 mk_data("out.txt", &function, left, right, 1000);
22 mk_graph("out.txt", "x", left, right, "y", -3, 3);
23
24 ans = bisection(&function, left, right);
25
26 printf("answer = %12.7e\n",ans);
27
28 return 0;
29 }
30
31 /*==========================================================*/
32 /* to be solved equation. f(x)=0 */
33 /*==========================================================*/
34 double function(double x){
35 double y;
36
37 y=x*cos(x)+sin(x)+exp(-x*x)+x*x-x-3;
38
39 return y;
40 }
41
42 /*==========================================================*/
43 /* bisection method f(x)=0 */
44 /*==========================================================*/
45 double bisection(double (*f)(), double left, double right){
46 double temp, mid;
47
48 /*---- left と right が逆の場合 -------*/
49
50 if(left > right){
51 temp = left;
52 left = right;
53 right = temp;
54 }
55
56 // while(right-left > EPSILON){
57 while(right-left > EPSILON){
58 mid = (left+right)/2.0;
59
60 if(f(left)*f(mid) >= 0){
61 left = mid;
62 }else{
63 right = mid;
64 }
65
66 }
67
68 return (left+right)/2.0;
69 }
70
71 /*==========================================================*/
72 /* make a data file */
73 /*==========================================================*/
74 void mk_data(char *a, double (*f)(double), double x1, double x2, int n){
75 double x, y, dx;
76 int i;
77 FILE *out;
78
79 dx = (x2-x1)/n;
80
81 out = fopen(a, "w");
82
83 for(i=0; i<=n; i++){
84 x = x1+dx*i;
85 y = f(x);
86
87 fprintf(out, "%e\t%e\n", x, y);
88 }
89
90 fclose(out);
91 }
92
93 /*==========================================================*/
94 /* make a graph */
95 /*==========================================================*/
96 void mk_graph(char *f, char *xlb, double x1, double x2,
97 char *ylb, double y1, double y2){
98
99 FILE *gp;
100
101 gp = popen("gnuplot -persist","w");
102
103 fprintf(gp, "reset\n");
104
105 /* ------- set x grid ---------*/
106
107 fprintf(gp, "set grid\n");
108
109 /* ------- set x axis ---------*/
110
111 fprintf(gp, "set xtics 1\n");
112 fprintf(gp, "set mxtics 10\n");
113 fprintf(gp, "set xlabel \"%s\"\n", xlb);
114 fprintf(gp, "set nologscale x\n");
115 fprintf(gp, "set xrange[%e:%e]\n", x1, x2);
116
117 /* ------- set y axis ---------*/
118
119 fprintf(gp, "set ytics 1\n");
120 fprintf(gp, "set mytics 10\n");
121 fprintf(gp, "set ylabel \"%s\"\n", ylb);
122 fprintf(gp, "set nologscale y\n");
123 fprintf(gp, "set yrange[%e:%e]\n", y1, y2);
124
125 /* ------- plat graphs ---------*/
126
127 fprintf(gp, "set terminal x11\n");
128
129 fprintf(gp, "plot \"%s\" using 1:2 with line\n", f);
130
131 fprintf(gp, "set terminal epslatex\n");
132 fprintf(gp, "set output \"function.eps\"\n");
133
134 fprintf(gp, "replot\n");
135
136 pclose(gp);
137 }
ホームページ: Yamamoto's laboratory
著者: 山本昌志 Yamamoto Masashi
2006-02-27
![\begin{picture}(18000,10800)(0,0)%
\put(1650,1650){\makebox(0,0)[r]{\strut{}-3}}...
...\put(14950,9675){\makebox(0,0)[r]{\strut{}''out.txt'' using 1:2}}%
\end{picture}](img30.png)